how to know if a pallet is safe:
- no signs of spills or leakage of items
- stamps that can be found:
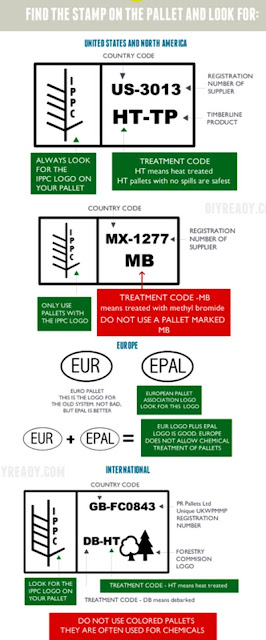
IPPC logo, International Plant Protection Convention, prevent spreading of invasive species and plant disease, pallets have to be treated. They regulate so wood products ensure that they meet the specifications for international shipping. They require treatment by one of the following methods:
1) Heat Treatment [HT] - heated for at least 30 min. at least at 132.8 °F /56° C -> Stamped with [HT]
2) Chemical Fumigation [MB] - fumigated with methyl bromide -> stamped with [MB], since March 2010 it has been banned.
3) Debarked [DB] - debarked under IPPC regulations, and many pallets have this stamp. Wood packaging materials must be debarked prior to being heat treated or fumigated to meet regulations.
4) Kiln Dried [KD] - dried by steaming in order to bringing all wood products to moisture content levels that will be subject to minimal moisture-related damage.
- other stamps:
Europe:
EUR: EURO pallet this is the logo for the old system, not bad, but EPAL is better.
EPAL: European Pallet Association Logo
EUR + EPAL: EUR logo plus EPAL logo is good. EUROPE DOES NOT ALLOW CHEMICAL TREATMENT OF PALLETS.
International:
GB-FC0843 - Country code + Registration Number+
IPPC logo
+
DB-HT - Treatment code
- do not use colored pallets, they are often used for chemicals
- what if there is no stamp or marking on the pallet? Most likely for domestic transport, and do not require an IPPC stamp because it is not for international transport. Most likely safe.
SUMMARY:
To use: DB, HT, KD, EPAL
Not to use: MB, EUR, colored pallets


No comments:
Post a Comment